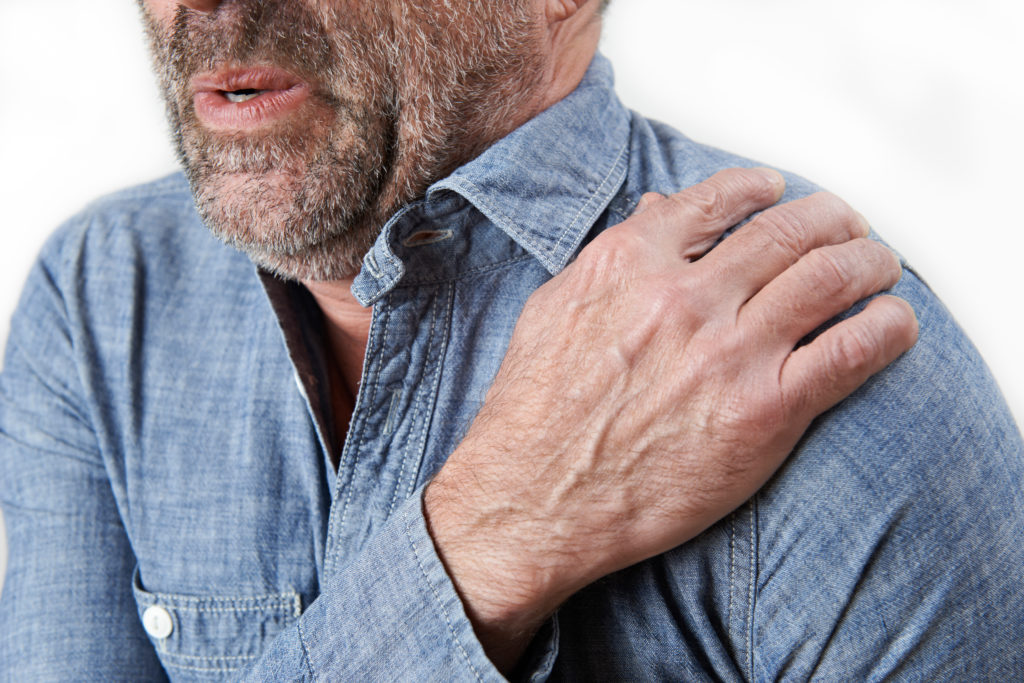
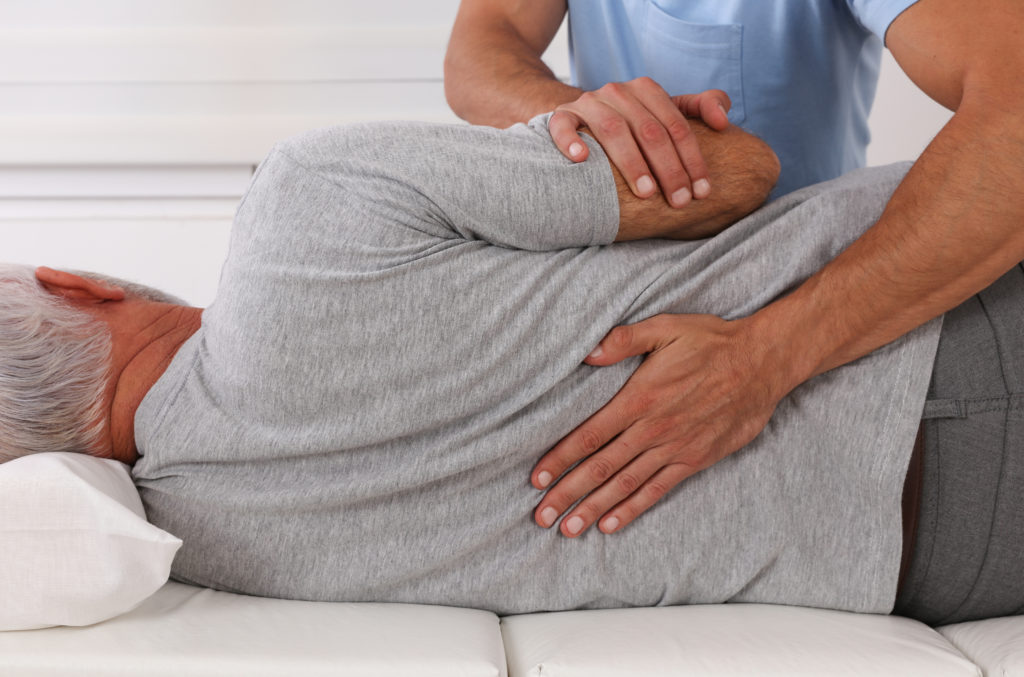
What is Shoulder Impingement?
The term shoulder impingement implies mechanical compression in the shoulder or wearing of the rotator cuff tendons. The rotator cuff maintains the humeral head in the socket, called glenoid, during normal shoulder function. It provides support to the shoulder during activity. The rotator cuff consists of four muscles that connect the scapula or shoulder blade to the humeral head or the upper part of the shoulder joint. The rotator cuff glides between the undersurface of the acromion and the humeral head. The acromion is the bone at the point of the shoulder.
How does shoulder impingement occur?
Any interference with the normal gliding function of the rotator cuff can cause impingement. Some of the common causes of impingement are degeneration and weakening of the tendon because of aging, the formation of bone spurs or inflammatory tissue in the space above the rotator cuff, and overuse injuries. Impingement is usually caused by overuse activities and can be seen among swimmers, pitchers, and tennis players.
How is shoulder impingement diagnosed?
Shoulder impingement can be diagnosed through a careful history and physical examination of the person. Usually, impingement occurs with pain in the shoulder that becomes worse with overhead activity and sometimes resulting in awakening in the night. A physician will be able to identify the condition by manipulating the shoulder in a particular way. He or she may ask for X-rays to evaluate the presence of bone spurs or the narrowing of the subacromial space.
Treatment of shoulder impingement
Treatment of impingement begins with the elimination of any factor that may be responsible for causing it, such as avoiding swimming, tennis or pitching. Your physician may prescribe anti-inflammatory nonsteroidal medication. However, the main treatment consists of exercises that can restore normal strength and flexibility to the shoulder girdle. Treatment also includes strengthening of the rotator cuff muscles and the muscles of the shoulder blade. The demonstration of exercises and program instruction may be taken up by a certified athletic trainer, a doctor or a skilled physiotherapist. Sometimes, a cortisone injection may also prove to be beneficial in treating this condition. In video below you see the technology we use in at our locations in Scarborough and Woodbridge.
Is surgery necessary?
In most cases of shoulder impingement, surgery may not be required. However, if the symptoms continue after non-surgical treatment, surgical intervention may become necessary. Surgery consists of removing tissue that is irritating the rotator cuff through open or arthroscopic techniques. Around 90% of cases are successful. The shoulder is the most mobile joint in the body, can perform a range of movements. It can turn in many directions. It allows you to lift the arm, rotate it, and reach above the head. However, this range of movement gives it less stable.
Are you concerned about symptoms of shoulder impingement or sports-related injury? Book a physiotherapy assessment at Simply Align Rehab – Cedarbrae Medical Center: 3630 Lawrence Ave E, Scarborough, ON M1G1P6 or at 200 Marycroft Ave, Unit #6, Woodbridge, ON, L4L 5X9
Shoulder dislocation
Our shoulder is one of the most mobile joints in our body. We are able to turn it in many directions. We can lift up our arms and reach up above our head and we can rotate it. However, this greater range of movement also results in the shoulder is less stable.
How does a shoulder dislocation happen?
Our shoulder is made up of three bones, 1) the humerus or upper arm bone, 2) the scapula or the shoulder blade and 3) the clavicle or the collarbone. Shoulder instability happens when the head of the humerus (upper arm bone) is forced out of the shoulder socket due to a sudden traumatic injury. If the shoulder gets dislocated, it is vulnerable and can cause repeat dislocations. When the shoulder slips out of its socket repeatedly, the condition is known as chronic shoulder instability. When the ball of the upper arm partially comes out of the socket it is known as subluxation. When the ball comes out completely from the socket the condition is known as complete dislocation.
What are the symptoms?
The most common symptoms of shoulder instability are pain that occurs due to shoulder injury, repeated shoulder dislocations, a constant sensation of the shoulder feeling loose, slipping in and out of the joint, or repeated instances of the shoulder giving out.
How is shoulder instability diagnosed?
A variety of tests are available in order to assess the instability in the shoulder or general looseness in ligaments. They include imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs. They help the physician in the diagnosis and identification of the underlying problem of the patient.
Treatment of shoulder instability
Initially, shoulder instability is treated with non-surgical options. However, if these non-surgical options do not relieve you of the pain and instability, then surgery may be required. Statistics show that every year around 70,000 shoulder dislocations occur and many of those who suffer are athletes.
Non-surgical Treatment
Non-surgical treatment usually takes many months of treatment before the results can be seen. Treatment includes modification of activities, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication, and physiotherapy.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery helps repair torn or stretched ligaments so that they can hold the shoulder joint in place. Surgery can repair the tearing of the front labrum from the socket (also known as bank hart lesions) by using suture anchors to reattach the ligament to the bone.
Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgery. Typically, the surgeon looks into the shoulder with a tiny camera and performs the surgery. Special tiny instruments are used to make small incisions and repair the soft tissues inside the shoulder.
Open Surgery
Open surgery requires making a larger incision over the shoulder and performing the surgery under direct visualization. This procedure is suitable for some patients. The shoulder may be immobilized for some time with a sling after the surgery. Once the sling is removed, the patient will have to do exercises to rehabilitate the ligaments. These exercises will help the person improve the range of motion in the shoulder and prevent scarring as the ligaments recover. Later, the patient will be asked to take up strengthening exercises as part of the rehabilitation plan. The shoulder is the most mobile joint in our body and can move in many directions. We can lift the arm, rotate it, and reach up over the head. However, due to the wide range of motions, our shoulder has less stability.
Are you looking for physiotherapy or a Chiropractor? If Yes, then visit Simply Align Rehab Physio in Scarborough/Toronto or Woodbridge/Vaughan or you can always call or text us for your Physiotherapy or Chiropractor needs in Toronto at (416) 438-3230 or For Physiotherapy or Chiropractor need in Vaughan (Woodbridge) at (905) 638-9840.