What is Scoliosis?
Scoliosis is a medical term used to denote the sideways or side-to-side curvature of the spine in either an “s” or “c” shape. Scoliosis is common among school growing children and can range from mild to severe. If a doctor has defined a clear cause of scoliosis, the curves are then defined as being structural or nonstructural.
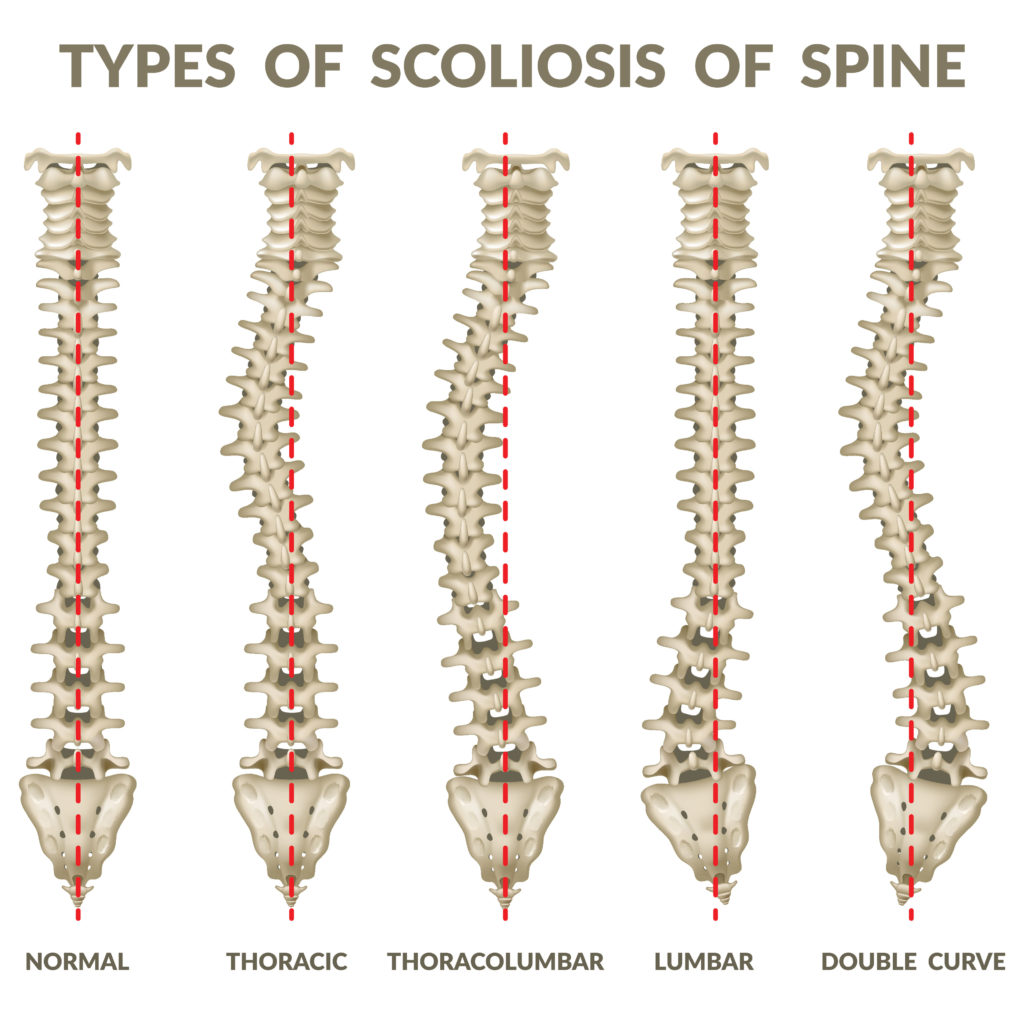
What is Nonstructural or Functional Scoliosis?
In nonstructural or functional scoliosis, the spine is normal and works properly but looks curved. This can be due to muscle spasms, appendicitis, or having one leg longer than the other. In nonstructural scoliosis, the curve may correct itself or can be corrected.
What is Structural Scoliosis?
When the curve of the spine is fixed and rigid and cannot be corrected, it’s called structural scoliosis. The cause of structural scoliosis can be unknown (idiopathic) or the result of another disease or condition such as Marfan syndrome, Cerebral palsy, Poliomyelitis, Muscular dystrophy, Birth defects, Injury, Infections, tumors, or metabolic disorders.
What Causes Scoliosis?
In most cases, scoliosis is idiopathic, meaning it has no known cause. There are some studies that suggest scoliosis may be hereditary, as the condition runs in families.
What are the Risk Factors?
Several risk factors, such as Age, Gender, and Genetics can increase your chance of developing scoliosis. Scoliosis is common in children with symptoms starting just before puberty, during the growth spurt. Gender: Although both boys and girls are equally likely to develop scoliosis, girls have a higher risk of developing more severe Scoliosis that requires treatment. Genetics: Some studies suggest scoliosis runs in families.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Scoliosis?
Symptoms of scoliosis vary depending on the symptoms. For example, One-shoulder looks higher than the other, One-shoulder looks more prominent than the other, One side of the hip is higher than the other, The waist looks flat on one side; The ribs look higher on one side when bending at the waist or the head does not look centered on the body. In more severe cases of scoliosis, people may experience heart and lung damage, making it difficult to breathe or Chronic back pain as the curve worsens.
Concerned about symptoms of scoliosis? Consult our expert physiotherapist in Scarborough, Toronto, or Woodbridge, Vaughan and book an assessment today.
Treating Scoliosis in Scarborough, Toronto!

Treatment for Scoliosis varies depending on the cause, severity, and likelihood of progression. A doctor monitors the condition with regular checkups every 4 to 6 months. Physiotherapy helps To improve conditioning and overall health, Bracing helps To prevent the progression of scoliosis in growing children and In severe cases Surgery (Spinal fusion surgery) is used to prevent scoliosis from getting worse. At Simply Align we use a specific protocol to stabilize scoliosis related issues.
Can Scoliosis Go Away By Itself?
Scoliosis is usually the result of a growth spurt and gets resolved with no bracing or surgery. However, it is important to seek the advice of a family doctor to make sure there is no serious underlying cause.
Can You Prevent Scoliosis?
Scoliosis cannot be prevented.
Are you looking for physiotherapy or a Chiropractor? If Yes, then visit Simply Align Rehab Physio in Scarborough/Toronto or Woodbridge/Vaughan or you can always call or text us for your Physiotherapy or Chiropractor needs in Toronto at (416) 438-3230 or For Physiotherapy or Chiropractor need in Vaughan (Woodbridge) at (905) 638-9840.
Also Read
| Degenerative Disc Disease (Intervertebral Disc Pain) | Low Back Pain |
| Low Back Osteoarthritis | Lumbar Spondylosis |
| Sciatica | Whiplash |
| Scoliosis | Upper Back and Shoulder Pain |