What is lumbar disc disease?
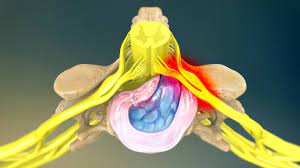
The backbone comprises of 33 vertebrae which are separated by spongy disc. There are 4 areas in which the spine is divided.
- Cervical spine: The first 7 vertebrae, are found in the neck
- Thoracic spine: The next 12 vertebrae, are found in the chest area
- Lumbar spine: The next 5 vertebrae, are found in the lower back
- Sacral spine: The lowest 5 vertebrae, are found below the waist, also includes the 4 vertebrae that make up the tailbone (coccyx)
There are 5 bony segments in the lumbar spine in the lower back area, that is where lumbar disc disease occurs.
- Bulging disc. With the passing time, fluid might start losing from the intervertebral disc and it might become dried out. Now when this will happen, the spongy disc will start becoming compressed. It is located between the bony parts of the spine and acts as a “shock absorber”. It will result in the breaking down of the tough outer ring. The nucleus, or the inside of the ring will now start bulging. This is known as bulging disc.
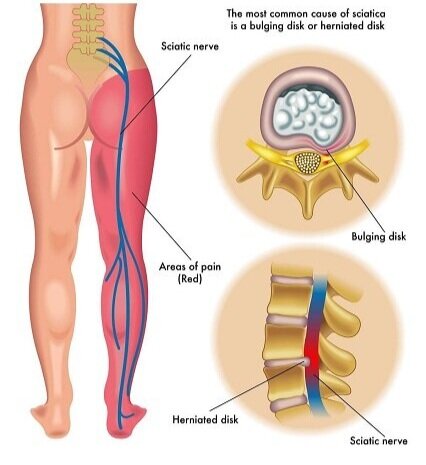
- Ruptured or herniated disc also known is disc protrusion. When the disc will continue to break down, or if there is continued stress on the spine, then the inner nucleus pulposus might start rupturing out from the annulus. This is called as ruptured, or herniated disc. The nerve roots which are situated just behind the disc space can be pressed by the fragments of the disc material. This may result in discomfort, frailty, numbness, or alterations in feeling.
The lower lumbar spine is where the majority of disc herniations occur, particularly between the L4-5 and L5-S1 levels, which are the fourth and fifth lumbar vertebrae and the fifth lumbar vertebra, respectively.
What causes lumbar disc disease?
The disc can start bulging or even herniating as a result of trauma or incorrect lifting. A significant factor is played by aging. As you age, your discs become harder and starts drying out. The strong fibrous outer wall of the disc could deteriorate. When it will come in contact with a nerve, the gel like nucleus might start expanding or explode through a tear in the disc wall. Early disc degeneration might be brought on by genetics, smoking or variety of professional and recreational activities.
Who is affected?
The people who are in their 30s and 40s are most likely to develop herniated discs, while people who are in their middle age and later years might be slightly more susceptible if they engage in strenuous physical activities.
One of the most common causes of lower back pain which is coupled with leg pain is lumbar disc herniation, which happens 15 times more frequently than cervical (neck) disc herniation. Only 1 to 2% of the time do disc herniations occur in the upper-to-midback (thoracic) region, in comparison to 8% in the cervical (neck) region.
What are the risks for lumbar disc disease?
Physical inactivity might result in weak back as well as abdominal muscles, which might not adequately support the spine, even though the most common risk factor is the age. The people who are not very physically active or engage in a lot of excessively demanding activities, generally suffer from back injuries. One another cause of back problems is the jobs that entail a lot of lifting and spinal twisting.
What are the symptoms of lumbar disc disease?
The location of the herniated disc and what the nerve root is pressing on can affect the symptoms of lumbar disc disease. Have a look at the most common symptoms of lumbar disc disease:
- There might be intermittent or continuous back pain. It can turn worse by movement, coughing, sneezing, or standing by extended amount of time
- Muscular spasm in the back
- Sciatica – It is a type of back or buttock discomfort which radiates down the leg, to the calf or the foot
- The muscles of the leg are weakened
- There might be tingling in the leg or foot
- Decreased knee or ankle reflexes
- Alternations in bladder or bowel function
Lumbar disc disease can resemble other conditions or medical problems. So it is important to always consult your healthcare provider for a check up.
How is lumbar disc disease diagnosed?
You might have one or more of the following tests in addition to a thorough medical history and physical exam:
- X-ray. It is a test which utilizes invisible electromagnetic energy beams to produce images of internal tissues, bones, and organs onto film. X-rays do not show discs and therefore disc herniations can be missed in x-rays.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It is a procedure which utilizes a combination of large magnets, radiofrequencies, and a computer to generate detailed images of organs and structures within the body.
- Myelogram. It is method that involves injecting dye in the spinal canal to make the structure visible on X-rays.
- The other names for computed tomography scans are CT or CAT scans. It is a kind of imaging which creates axial or horizontal images of the body, which are also called as slices, using X-rays and modern technologies. CT scan helps to see any aspect of the body, including the bones, muscles, fat, and organs.
- Nerve conduction velocity testing and needle EMG. During this test speed of signals traveling through your nerves and muscles is measured and reduction of speed may mean impingement by a disc herniation.
How is lumbar disc disease treated?
The initial line of lumbar disc disease treatment is generally conservative therapy. This might include a mix of the following:
- Education on good body mechanics (to lessen the possibility of the pain getting worse or the disc getting damaged)
- Physiotherapy and chiropractic treatments
- Exercise regimens and core stabilizations
- Weight control
- Medicines that reduce pain and relax muscles
If you find out that none of these remedies work, you may need surgery to have the herniated disc removed. Surgery is done under general anesthesia. Your surgeon will cut your lower back over the herniated disc’s location. Bone from the back of the spine may need to be removed to access the disc. The herniated portion of the disc as well as any extra loose fragments from the disc space will be surgically removed by your surgeon.
Your ability to move around after the surgical procedure can be limited while you heal in order to prevent another disc herniation. If there are any limitations, then it will be discussed with you by your surgeon.
In the video below you can see Spina Decompression Therapy that may pull the discs back into place and reduce herniation. This technology is available at both of our clinics at Simply Align Physio-Chiro in Toronto (Scarborough) and Vaughan (Woodbridge).
What are the complications of lumbar disc disease?
The regular activities can be interfered by the Lumbar disc disease which can cause back and leg pain. It might result in issues with bowel and bladder control as well as numbness or paralysis in the legs.
Can lumbar disc disease be prevented?
The risk of developing lumbar disc disease can be reduced by eating healthily, exercising frequently, and adopting good posture.
Living with lumbar disc disease
Keep in mind that Conservative therapy needs patience; but following your treatment plan can decrease the back pain and then it can also prevent the possibility of further damage or disc injury. To be effective, both surgical procedures and conservative methods can take time.
Recovery & prevention
8 out of 10 people experience back pain at some point in their lives, and it generally resolves within 6 weeks. A positive outlook, consistent exercise, and a fast return to work at very essential elements of recovery. It is in your best advantage to return to a modified (light or restricted) duty if your usual job cannot be done at first. Such activities might be prescribed by your doctor for brief periods of time.
Below you can review the video about how not to aggravate your disc herniation.
How can physiotherapy help with Lumbar Disc Herniation?
The main goal of our physiotherapy treatments is to relieve pain, help in back movement, and at the same time promote good posture. Our physiotherapist will help you in finding positions as well as movements that help in reducing pain. Treatments like tecar therapy, shockwave, and laser may be performed. Lumbar traction may also be used initially, to ease symptoms of lumbar disc herniation. Additionally, physiotherapists can also apply manual techniques like spine manipulation or massage. These types of treatments are mostly used to help in reducing pain as well as inflammation so you can quickly get back to your regular activities. Your physiotherapist will also help you by showing you how to protect your spine while performing routine activities. It will help you in learning about a good posture and how it affects the long-term health of your spine.
In the video below you see spinal decompression therapy that can help with herniated discs as well as core stability exercises.
Are you looking for physiotherapy or a Chiropractor? If Yes, then visit Simply Align Rehab Physio in Scarborough/Toronto or Woodbridge/Vaughan or you can always call or text us for your Physiotherapy or Chiropractor needs in Toronto at (416) 438-3230 or For Physiotherapy or Chiropractor need in Vaughan (Woodbridge) at (905) 638-9840.
