What is Bursitis?

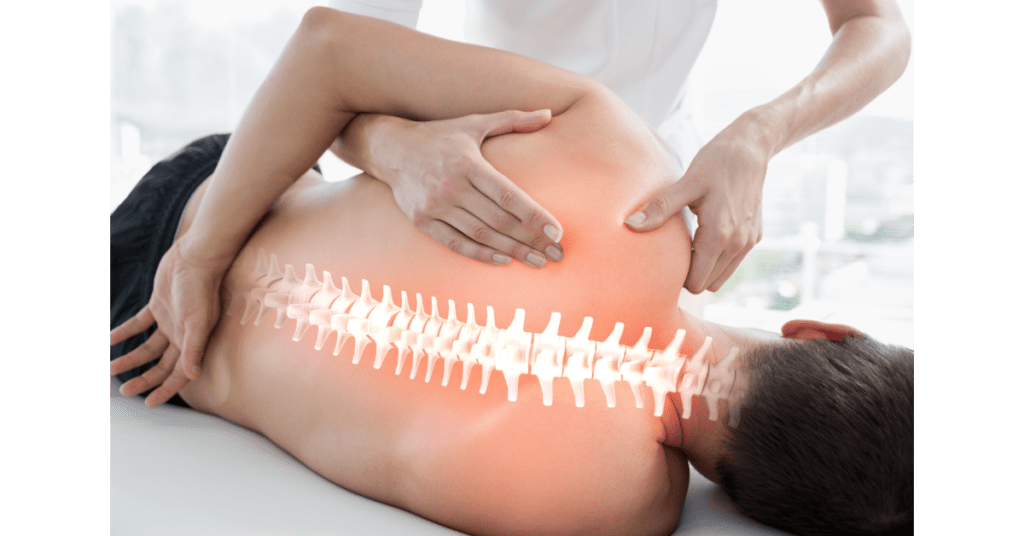
Bursae refer to the small fluid-filled sacks between the tendon and bones. Bursitis is the condition in which the bursae are swollen and inflamed. This can be caused by a bacterial infection, injury, or repetitive movements that irritate the bursae. Since it can affect many different parts of the body, it is known by different names, like ‘tennis elbow’, ‘weaver’s bottom’, ‘student’s elbow’, ’housemaid’s knee’, ‘clergy man’s knee’ or ‘soldier’s heel’.
Where Can You Get Bursitis?
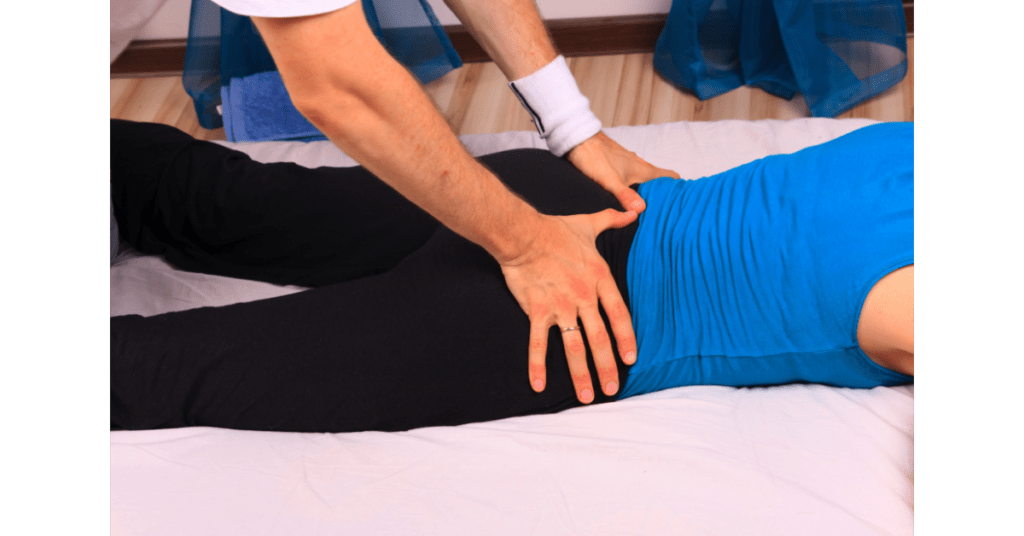
Our body has over 150 bursae. Typically, bursitis occurs in locations where there is movement. For example, subacromial bursitis occurs in the rotator cuff of the shoulders. The cause of subacromial bursitis is prolonged overhead activities, such as heavy lifting, playing sports, or an injury. Olecranon bursitis or elbow bursitis occurs in the elbow region and can be caused due to a hard blow to the elbow, a prolonged period of leaning on the elbow, or an injury. Iliopsoas bursitis (or hip bursitis) is the largest in the body and is caused due to a hip injury, overuse of the hip or inflammatory diseases, etc. Ischial bursitis or bursitis of the buttocks is also known as the weaver’s bottom. This can be caused due to prolonged sitting on a hard surface, due to falling on the bottom or an infection. Trochanteric bursitis (outside of the hip) occurs when there is overuse of the hip, poor posture or a hip injury. Suprapatellar, Prepatellar, Infrapatellar and Pes Anserine Bursitis are four bursae locations in the knee. All these bursae can develop bursitis due to long periods of kneeling, hitting the knee, arthritis or infections. Heel bursitis is known as Achilles and Retrocalcaneal bursitis and can occur due to repetitive use, injury or due to rheumatoid arthritis. Bursa is a small sack filled with lubricating liquid known as synovial fluid that serves as a cushion between the muscles, tendons and bones. This fluid lubricates the joints and enables them to move freely. Bursitis occurs when the bursae get inflamed. Bursitis refers to the disease or inflammation of the bursa as the name itself implies.
What Causes Bursitis?
There are several causes for bursitis, the most common being overuse or repetitive movement and pressure on the joint. For example, doing a repetitive motion for hours at a stretch or strain due to lifting and moving heavy items. Trauma can be caused due to hitting or bumping against an object or leaning on a desk and putting continuous pressure on the joint. Other causes include infections, auto-immune disorders, injury or trauma to the joint, scoliosis and inflammatory conditions like scleroderma, lupus, gout and rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammatory diseases, like gout and rheumatoid arthritis can also cause bursitis.
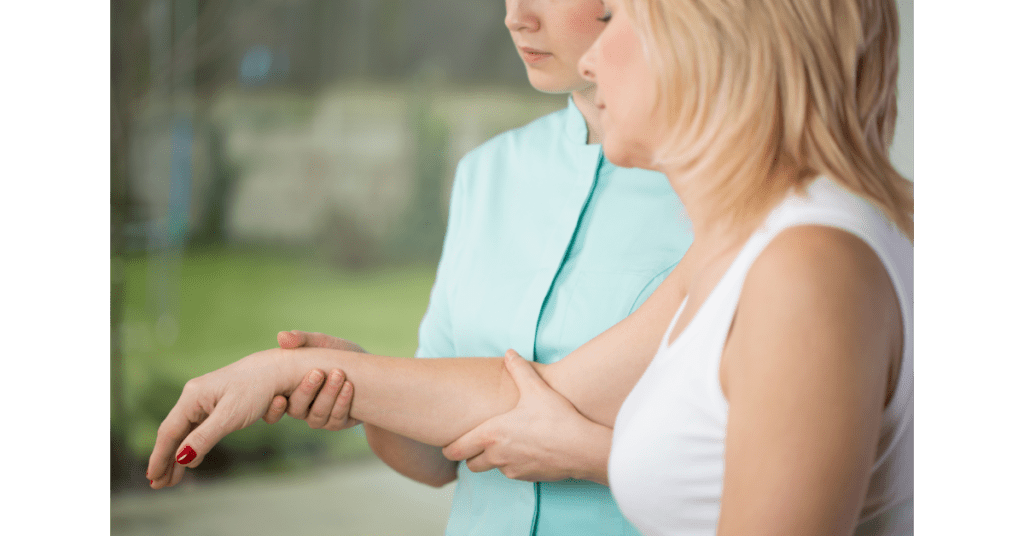
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Bursitis?
The signs and symptoms of bursitis vary depending on the joint affected and the cause. Generally, bursitis results in inflammation, tenderness and pain around the affected joint, which affects the tendons, ligaments, bursae and muscles around it. One may notice a lump on the affected bursa or a tender, painful and stiff joint. The joint usually hurts when pressed and the pain becomes worse with movement. The joint may become red and swollen, making mobility difficult. A sharp or shooting pain may occur when the joint it moved.
Are you looking for physiotherapy or a chiropractor? Book an assessment today at EAST (Scarborough) 3630 Lawrence Ave E, Scarborough, ON M1G 1P6 or 200 Marycroft Ave UNIT 6, Woodbridge, ON L4L 5X9, Canada.
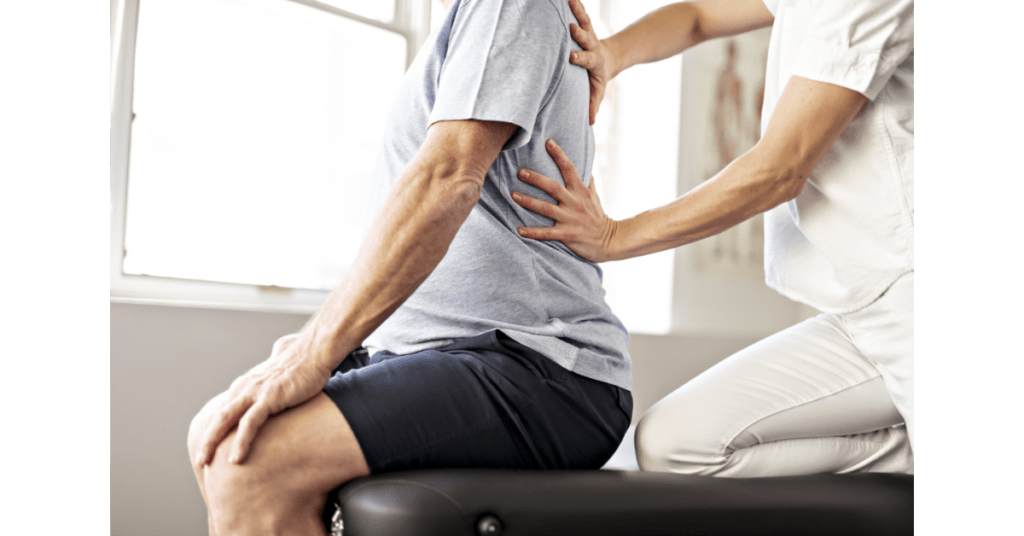
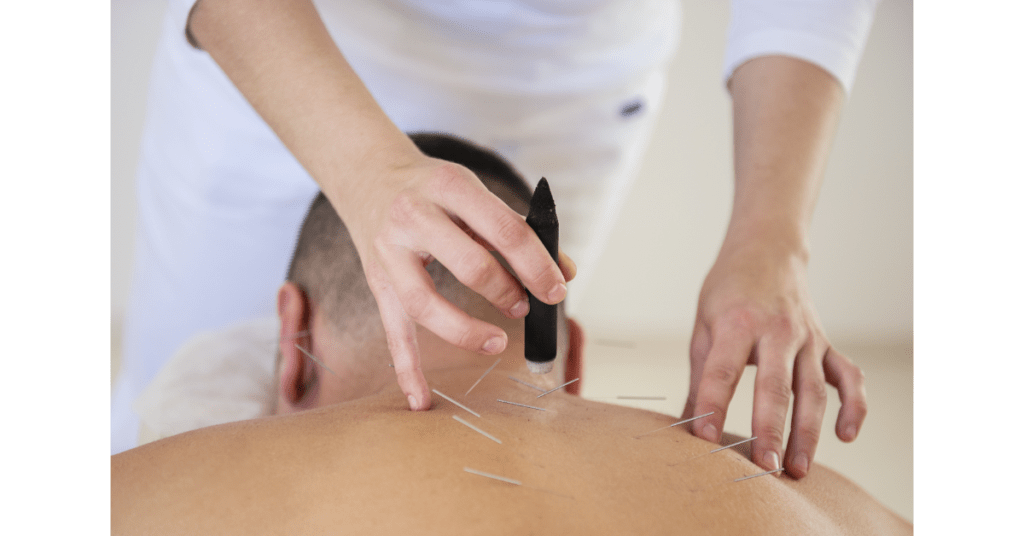
How is Bursitis Treated?
Treatment of bursitis is done either at home or in the clinic. Usually at home remedies consist of taking rest, applying ice or avoiding activities that aggravate the condition. If the symptoms continue to persist you will need to consult a physiotherapist, who will prepare a treatment plan to match your specific concerns. The physiotherapist will evaluate the condition, identify the causes and advise accordingly. Treatment may include activity modifications, functional retraining, strengthening exercises, manual therapy and range of motion exercises. Manual therapy includes joint and soft tissue mobilizations. The physiotherapist may also provide a personalized exercise plan or recommend the use of an assistive device, orthotics, splint or pain relieving modalities like therapeutic ultrasound, heat and ice therapy. Consult a physiotherapist now. At our clinic we have notice by using Simply Align Technique which includes advance physical modalities, activity modification and specific exercises we have faster, longer lasting results with reduced healing time. In the video below you see the combination of three different machine, Radio Frequency Tecar therapy as well as shockwave followed by laser for treatment of knee bursitis.
Can Bursitis go away?
Yes. Bursitis can go away with home treatments like taking pain-relieving medication, applying cold therapy or resting the affected joint. If the condition is due to repetitive tasks and overuse, it may come back if there is no modification in activity.
Can you prevent Bursitis?
Yes. However, if your job requires you to perform repetitive movements, or if you have an auto-immune disorder, it is best to consult a physiotherapist and explain the specific requirements. Some steps that one can take to avoid bursitis are practicing good posture, warming up before exercises and following new exercise routines.
Are you looking for physiotherapy or a Chiropractor? If Yes, then visit Simply Align Rehab Physio in Scarborough/Toronto or Woodbridge/Vaughan or you can always call or text us for your Physiotherapy or Chiropractor needs in Toronto at (416) 438-3230 or For Physiotherapy or Chiropractor need in Vaughan (Woodbridge) at (905) 638-9840.